Introduction
When deploying wireless systems—whether for industrial IoT, broadband, or remote monitoring—most attention goes to antennas, routers, and modems. But there’s one often-overlooked factor that can quietly undermine your entire setup: RF cable length and signal loss. In this article, we explain how cable length affects wireless performance and how to prevent signal degradation with best-practice installation.
What Happens When RF Cable Length Increases?
RF cables carry signals from devices to antennas. However, as the length of the cable increases, attenuation (signal loss) becomes inevitable. This means a weaker signal reaches your antenna or modem, leading to:
- Shorter effective range
- Slower data rates
- Intermittent or unstable connections
High-frequency signals are particularly vulnerable. For instance, at 2.4 GHz, a low-quality cable could lose up to 50% of signal strength over just a few meters.
Understanding Cable Loss (Attenuation)
Cable loss is measured in dB (decibels) per unit length. The higher the frequency or the longer the cable, the greater the loss. Key factors influencing attenuation include:
- Cable type and quality: Low-loss cables significantly outperform thinner, cheaper options.
- Frequency: Higher frequencies suffer greater losses.
- Environmental conditions: Heat, moisture, and physical wear increase loss over time.
A Quick Look at Coaxial Cable Structure
Coaxial cables are designed to transmit high-frequency signals with minimal loss and interference. Their structure includes several key layers:
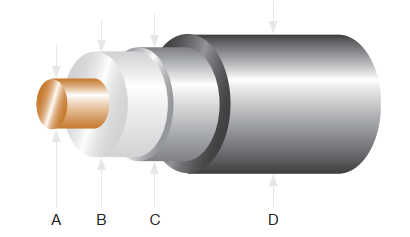
A. Inner conductor – Typically made of copper or copper-clad steel, this central wire carries the RF signal.
B. Dielectric insulator – Surrounds the inner conductor to maintain spacing and reduce signal degradation.
C. Shielding – A metal foil and/or braided mesh that blocks external electromagnetic interference (EMI).
D. Outer jacket – A tough, weather-resistant coating that protects the cable from physical and environmental damage.
This layered design helps coaxial cables maintain signal integrity, especially when high-quality materials and proper installation methods are used.
Best Practices to Minimise Cable Loss
- Choose the Right Cable Type
Select cables engineered for minimal attenuation. For high-frequency or long-distance applications, premium low-loss cables are a must.
- Keep Cable Lengths as Short as Possible
Avoid excess cabling wherever possible. Every additional meter can eat into your signal strength, so plan installations carefully.
- Use Quality Connectors and Proper Termination
Poorly installed or low-grade connectors introduce additional loss and reflections. Invest in good quality components and professional installation if necessary.
- Protect Cables from Environmental Damage
Use UV-resistant and weatherproof cables for outdoor deployments. Even indoor cables benefit from proper routing and shielding to avoid mechanical stress and electromagnetic interference.
- Test and Measure
Use RF testing equipment to verify cable performance after installation. Identifying issues early can save significant troubleshooting time later.
When to Use Cable Extenders or Amplifiers
If unavoidable long cable runs are required, consider using RF amplifiers or repeaters to boost the signal. Alternatively, repositioning equipment to reduce cable distance may be a better long-term solution.
Conclusion
Don’t let cabling be the weak link in your wireless infrastructure. By understanding how signal loss occurs and taking the right steps, you can maintain reliable, high-performance connectivity across your applications.
Need help choosing the right RF cable or connectors? Get in touch with Siretta for expert guidance and a wide range of high-spec connectivity solutions.
Have any questions? Please contact one of the Sales Team today [email protected]