To identify the ideal Industrial Router for your application we have developed the Router Selector Tool which is a configurable filter to narrow down the results to match your exact requirements.
5G NR is the fifth generation of wireless technology, where “NR” stands for New Radio interface, a radio access technology for cellular networks — a physical connection method for radio-based communication. Other kinds of radio access technologies include Bluetooth, Wi-Fi and 4G LTE.
5G NR is designed to support fibre-equivalent bandwidth transmissions required for data demanding applications like streaming video, as well as low-bandwidth transmissions used in machine-to-machine communications at increased capacity where needed.
5G NR will also support transmissions with extremely low latency requirements – for example applied to vehicle-to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure communications which is a vital prerequisite in those settings
Like its predecessors, the 5G NR standard was created by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP).
The 5G NR standard supports a number of low to high-frequency bands.
Frequency range 1: Includes frequency bands that are typically less than 6GHz (410 MHz to 7125 MHz).
Frequency range 2: Covers bands with a low range combined with a high bandwidth. (Typically 24250 MHz to 52600 MHz).
Benefits of 5G NR
In a growing connected world, 5G will certainly play a major role in industries and society including more capacity for wireless users, improved data rates and more importantly low lag and latency.
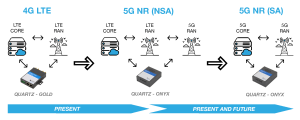
5G NR deployment modes
As 5G NR is being rolled out there are currently 2 Deployment Modes that are implemented. The two modes depends on several factors, including the existing infrastructure.
Non-Standalone (NSA)
Essentially, a “Hybrid”, as some of the existing 4G LTE infrastructure stays in place, while the radio frequency side is 5G NR. Advantages is a more speedier rollout as the current 4G facilities are reused. Non-Standalone 5G NR will provide increased data-bandwidth by using two new radio frequency ranges:
Frequency Range 1 (450 MHz to 6000 MHz) – This band overlaps with 4G LTE frequencies and is called as sub-6 GHz. Bands are numbered from 1 to 255.
Frequency Range 2 (24 GHz to 52 GHz) – This is the mm-Wave frequency band. Bands are numbered from 257 to 511.
Standalone (SA)
For standalone mode, the full 5G NR technical standard is deployed. No residual 4G technical underpinnings are involved. It deploys the new 5G Packet Core architecture instead of relying on the 4G Evolved Packet Core to allow the deployment of 5G without the LTE network. It is expected to have lower cost, better efficiency, and to assist development of new use cases. However, initial deployment might see slower speeds than existing network due to the allocation of spectrum.
Network Slicing
5G network slicing allows MVNO and operators to use a portion of the 5G network spectrum to split and serve various use-cases, including mobile networking, smart homes, IoT, and inventory management. This enables service providers to tailor packages to customers needs for “Mission Critical” objectives like remote surgery for the medical industry.
5G network slicing supports enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), which aims at maximizing the network speeds and data rates while having an acceptable QoS, including reliability and packet-error rates. This portion of the “Slice” will most certainly benefit data demanding applications.
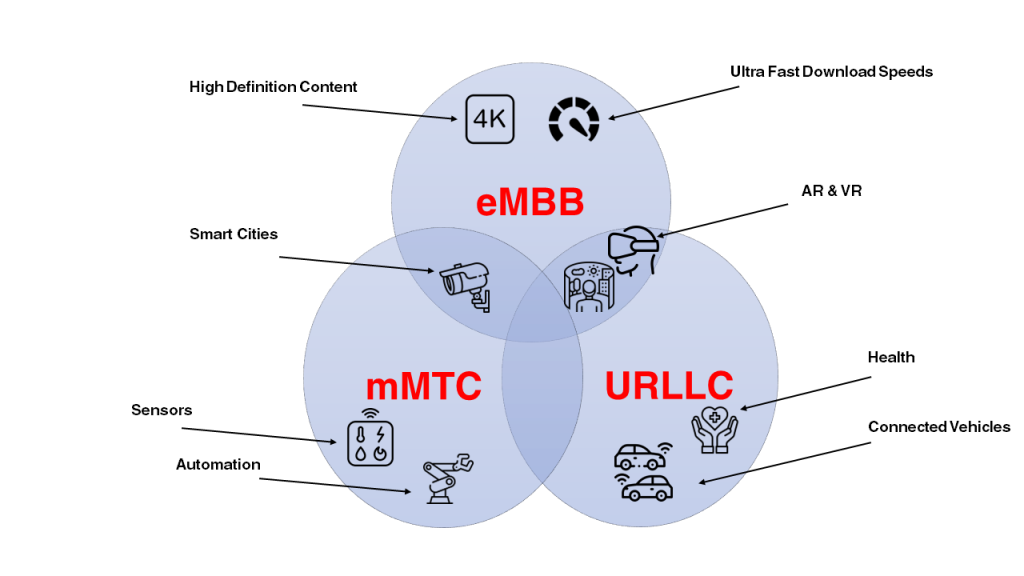
There are three main primary use cases within the 5G NR
Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB): Bandwidth-driven use cases needing high data rates across a mobile wide coverage area. These include, 4K Media, AR and VR applications.
Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communications (URLLC): Lowest possible latency and high network reliability for critical applications like autonomous vehicle, remote surgery/healthcare, or time-critical factory automation (e.g. semiconductor fabrication).
Massive Machine Type Communications (mMTC): Providing connectivity to a large number of devices that transmit intermittently a small amount of traffic such as Smart factories.
The future of 5G NR is certainly exciting as this 5th generation of cellular technology is constantly evolving and dynamic that promises ground-breaking new capabilities and to unlock the potential of technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Extended Reality (XR) and the Internet of Things (IoT).
With the traits of low latency, increased spectrum and throughput. 5G technology is truly a key enabler of new B2B opportunities and new emerging markets.
Siretta offers these solutions to solve your IoT and IIoT challenges. Including Modems, Routers and a vast array of Antennas to keep your world connected.
The table below shows all of the defined bands and the associated frequencies used with 5G NR network.
A2: Denotes UE Receive
A3: Denotes UE Transmit
| Band Number | 5G Mode | 5G Common name | Frequency (MHz) | Uplink[A 2] (MHz) | Downlink[A 3] (MHz) |
| n1 | FDD | IMT | 2100 | 1920 – 1980 | 2110 – 2170 |
| n2 | FDD | PCS | 1900 | 1850 – 1910 | 1930 – 1990 |
| n3 | FDD | DCS | 1800 | 1710 – 1785 | 1805 – 1880 |
| n5 | FDD | CLR | 850 | 824 – 849 | 869 – 894 |
| n7 | FDD | IMT‑E | 2600 | 2500 – 2570 | 2620 – 2690 |
| n8 | FDD | Extended GSM | 900 | 880 – 915 | 925 – 960 |
| n12 | FDD | Lower SMH | 700 | 699 – 716 | 729 – 746 |
| n13 | FDD | Upper SMH | 700 | 777 – 787 | 746 – 756 |
| n14 | FDD | Upper SMH | 700 | 788 – 798 | 758 – 768 |
| n18 | FDD | Lower 800 (Japan) | 850 | 815 – 830 | 860 – 875 |
| n20 | FDD | Digital Dividend (EU) | 800 | 832 – 862 | 791 – 821 |
| n24 | FDD | Upper L‑Band (US) | 1600 | 1626.5 – 1660.5[B 2] | 1525 – 1559[B 3] |
| n25 | FDD | Extended PCS | 1900 | 1850 – 1915 | 1930 – 1995 |
| n26 | FDD | Extended CLR | 850 | 814 – 849 | 859 – 894 |
| n28 | FDD | APT | 700 | 703 – 748 | 758 – 803 |
| n29 | SDL | Lower SMH | 700 | N/A | 717 – 728 |
| n30 | FDD | WCS | 2300 | 2305 – 2315 | 2350 – 2360 |
| n34 | TDD | IMT | 2100 | 2010 – 2025 | |
| n38 | TDD | IMT‑E[B 4] | 2600 | 2570 – 2620 | |
| n39 | TDD | DCS–IMT Gap | 1900 | 1880 – 1920 | |
| n40 | TDD | S-Band | 2300 | 2300 – 2400 | |
| n41 | TDD | BRS | 2500 | 2496 – 2690 | |
| n46 | TDD | U-NII-1–4 | 5200 | 5150 – 5925 | |
| n47 | TDD | U-NII-4 | 5900 | 5855 – 5925 | |
| n48 | TDD | CBRS (US) | 3500 | 3550 – 3700 | |
| n50 | TDD | L‑Band (EU) | 1500 | 1432 – 1517 | |
| n51 | TDD | L‑Band Extension (EU) | 1500 | 1427 – 1432 | |
| n53 | TDD | S band | 2400 | 2483.5 – 2495 | |
| n65 | FDD | Extended IMT | 2100 | 1920 – 2010 | 2110 – 2200 |
| n66 | FDD | Extended AWS | 1700 – 2100 | 1710 – 1780 | 2110 – 2200[B 7] |
| n67 | SDL | EU 700 | 700 | N/A | 738 – 758 |
| n70 | FDD | Supplementary AWS | 2000 | 1695 – 1710 | 1995 – 2020 |
| n71 | FDD | Digital Dividend (US) | 600 | 663 – 698 | 617 – 652 |
| n74 | FDD | Lower L‑Band (US) | 1500 | 1427 – 1470 | 1475 – 1518 |
| n75 | SDL | L‑Band (EU) | 1500 | N/A | 1432 – 1517 |
| n76 | SDL | Extended L‑Band (EU) | 1500 | N/A | 1427 – 1432 |
| n77 | TDD | C-Band | 3700 | 3300 – 4200 | |
| n78 | TDD | C-Band | 3500 | 3300 – 3800 | |
| n79 | TDD | C-Band | 4700 | 4400 – 5000 | |
| n80 | SUL | DCS | 1800 | 1710 – 1785 | N/A |
| n81 | SUL | Extended GSM | 900 | 880 – 915 | N/A |
| n82 | SUL | Digital Dividend (EU) | 800 | 832 – 862 | N/A |
| n83 | SUL | APT | 700 | 703 – 748 | N/A |
| n84 | SUL | IMT | 2100 | 1920 – 1980 | N/A |
| n85 | FDD | Extended Lower SMH | 700 | 698 – 716 | 728 – 746 |
| n86 | SUL | Extended AWS | 1700 | 1710 – 1780 | N/A |
| n89 | SUL | CLR | 850 | 824 – 849 | N/A |
| n90 | TDD | BRS | 2500 | 2496 – 2690 | |
| n91 | FDD | DD (EU) L-Band (EU) | 800 – 1500 | 832 – 862 | 1427 – 1432 |
| n92 | FDD | DD (EU) L-Band (EU) | 800 – 1500 | 832 – 862 | 1432 – 1517 |
| n93 | FDD | Extended GSM L-Band (EU) | 900 – 1500 | 880 – 915 | 1427 – 1432 |
| n94 | FDD | Extended GSM L-Band (EU) | 900 – 1500 | 880 – 915 | 1432 – 1517 |
| n95 | SUL | IMT | 2100 | 2010 – 2025 | N/A |
| n96 | TDD | U-NII-5–9 | 6000 | 5925 – 7125 | |
| n97 | SUL | S-Band | 2300 | 2300 – 2400 | N/A |
| n98 | SUL | DCS–IMT Gap | 1900 | 1880 – 1920 | N/A |
| n99 | SUL | Upper L‑Band (US) | 1600 | 1626.5 – 1660.5[B 2] | N/A |
| n101 | TDD | Rail Mobile Radio (RMR) | 1900 | 1900 – 1910 | |
| n102 | TDD | U-NII-5 | 6200 | 5925 – 6425 |
5G NR Capable Range of Industrial Routers
Dual Port Gigabit Ethernet 5G NR Router (GL)

QUARTZ-GOLD-5G Global NR Gigabit Ethernet, 2.4G + 5G Wi-Fi and RS232 Serial
Quad Port Gigabit Ethernet 5G NR Router (GL)

QUARTZ-ONYX Global 5G NR Gigabit Ethernet, 2.4G + 5G Wi-Fi and RS232/485 Serial
Quad Port Gigabit Ethernet 5G NR Router (GL) with GPS

QUARTZ-ONYX Global 5G NR Gigabit Ethernet, 2.4G + 5G Wi-Fi and RS232/485 Serial
